Osteocartilage degeneration is a degenerative destructive lesions of the spine, including failure of the vertebrae, arthroscope, ligament instrument and intervertebral disc. In all countries, the disease is average enough – from 45% to 85% of the population suffers from it. The onset of osteochondrosis occurs in patients over the age of 30-35, and cases of early onset of the disease are known. The frequency of men and women is roughly the same.
reason
There is no unified cause of osteochondrosis development. There are a large number of causal factors. The main contents are as follows:
- Spine injury (fracture, bruising, dislocation);
- Genetic tendency;
- Foot diseases that cause spinal overload - this includes flat feet, changes and deformation of the feet, valgus deformation of the feet;
- Wearing close and uncomfortable shoes for a long time (and also causes spinal overload);
- Overweight and obese;
- age-related changes;
- A sedentary lifestyle;
- Athletes who suddenly give up training and lessons;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Spine curvature (Kyphosis, Lordosis, scoliosis);
- Professional features - weightlifting, frequent turns and body twitching, in uncomfortable body position;
- Frequent and prolonged hypothermia;
- pressure;
- Specific climates in places of residence and workplace - low air and high humidity.
The development of the disease begins when exposed to one or more causal factors. Habits divide it into four main stages:
- Phase 1. The amount of water in the core of the intervertebral disc is reduced, it becomes flatter and the distance between the vertebrae is reduced. The cartilage covers smaller cracks.
- Phase 2. As the distance between the vertebrae decreases, the muscles and ligaments of the vertebrae occur. This causes the pathological mobility of the vertebral body to cause its displacement.
- Stage 3. Due to the progressive process of the spine, the intervertebral disc compression (herding), and subluxation of the vertebrae occurs.
- Stage 4. Between the vertebrae, bone spikes (bone plants) appear, aiming to eliminate vertebrae mobility and prevent dislocation. Over time, there were so many of them that the affected vertebrae completely lost their mobility. In this case, a series of blood vessels and nerves pass by and leave the spine near the vertebrae.
In the first and final stages of the clinical manifestation of the disease (pain), the patient did not.
Classification
There are many categories of osteochondrosis. Every doctor chooses the one he or she is most easily accepted. The following categories are most commonly used:
Category of spinal failure:
- Cervical osteochondrosis;
- Sternum chondrochondrosis;
- Lumbar bone osteochondral disease;
- coronary osteochondrosis;
- Widespread (common) osteochondrosis - affects 2 or more spines.
Classified by degree of change in the disc (radiology stage):
- Stage 0 - No disk changes;
- Phase 1 - Small changes, including the largest internal tears;
- 2 stages - Severe changes in the disk while maintaining the outer surface;
- Stage 3 - The entire disk is completely affected (cracks will spread to the outer surface, from disks inside the vertebrae, etc. ).
Classified by clinical manifestations and degree of impairment in spinal function:
- Stage 1 - The function of the spine has not changed and the patient feels mild pain when the lesion is changed;
- 2 stages - The function of the spine is disturbed (the occurrence of sublususes of the vertebral body, the herniation of the intervertebral disc, the clamping of the nerves), and the pain at the damaged area is exacerbated;
- Stage 3 - spinal deformation, hernia of the intervertebral disc occurs, obvious pain;
- Stage 4 - The patient is difficult to move, the spine has reduced mobility and is painful during the slightest movement. The patient has a disability.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
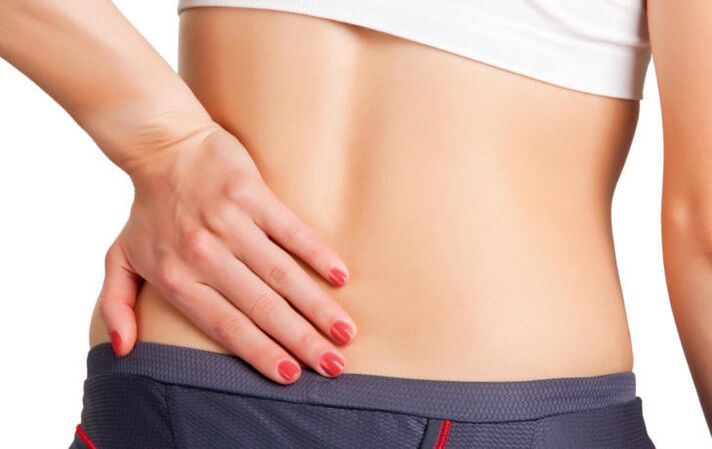

The symptoms of osteochondrosis depend on the area where the spinal column is damaged and the extent of the disease occurring therein.
For extended clinical maps of cervical spinal osteochondrosis, the following signs are characteristic:
- Violation of vision;
- Dizziness;
- Tinnitus;
- The appearance of the "flies" and colorful spots that flash in front of your eyes;
- Hearing loss;
- Headache in the nape of the neck, temporal lobe and apical area can be exacerbated when moving the cervical spine;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Snoring;
- the hoarseness of the voice or its decay;
- Numbness and loss of sensitivity on the skin of the face, neck and hands;
- Tooth damage;
- Blood Pressure Committee.
For osteocartilage of the thoracic vertebrae, the following symptoms are characterized:
- Heart pain, persisting for a long time, pain or pressure, is usually sharp, sewn, sharp, and the patient can show specific pain points;
- Numbness in the skin on the chest, abdomen and back;
- Spine pain, especially pain between shoulder blade bones, is strongly expressed;
- Pain when raising your hand;
- Sharp and deep breathing pain, then added as you exhale;
- Pain, discomfort and tilting in any direction during body tilt.
The following symptoms are characterized by lumbar vertebrae and bone spine:
- soreness in the lumbar and s-bone (lumbar) areas, which can be given in the form of one or two legs and are enhanced with any spinal movement in the affected area;
- The legs freeze for other parts of the body at a comfortable temperature;
- The back muscles, especially the waist area, are almost constant tension;
- A numb feeling, crawling chicken skin s and tingling skin on hips and buttocks;
- Veins on the legs;
- Violating male effectiveness;
- Increase sweating;
- Pale skin on the legs;
- Women have irregular menstruation.
With prolonged and neglected osteochondrosis, patients are worried only about the possibility of movement on a particular spine when the affected vertebrae fuses with each other, and often, pain usually decreases or completes the leaves.
diagnosis
First, the doctor investigated and examined the patient and established a preliminary diagnosis. For confirmation, other inspection methods are assigned. Due to osteocartilage degeneration, they are only instrumental because the laboratory (test) does not show any confirmed changes.
The main diagnostic methods include the following:
- X-ray examination. Allows you to determine the extent of damage to the vertebrae, its location, bone formation. With an indirect approach, you can determine the condition of the bone channel and disc;
- Computed tomography (CT). Allows you to determine the condition of the disc, its structure and shape, deformation of the vertebrae, and compression of nerve ends and roots;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Allows you to identify smaller violations in the spine and make provisions if the controversial issue remains CT;
- Ultrasound program. You can identify the extent of blood flow in the blood vessels feeding the spinal cord and other organs;
- Bone marrow science. A spinal X-ray method using contrast substances. Allows you to identify disc hernia.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Conservative treatment
In the treatment of osteocartilage, conservative treatments are mainly used. In this case, the approach to each patient should be individual and complex. Conservative treatments can be divided into 4 main groups:
- Drug treatment;
- Physiotherapy;
- hydrotherapy;
- Diet (the basics of proper nutrition).
Drug treatment for osteochondrosis
During the worsening period, medications used to treat osteochondrosis must be used. They lead to reduced symptoms and also certain causal factors that affect the development of the disease. The main drug groups used to treat osteocartilage:
- NSAID. NSAIDs have anesthetic, anti-inflammatory effects and also reduce the elevation of affected tissues in the spine and its structure. The first day of the disease exacerbated was prescribed in the form of an injection for obvious symptoms. The frequency of use is 1-2 times a day. Afterwards, if necessary, they switch the treatment rate to 10-30 days of medication. Admission frequency is 1 to 4 times a day. Likewise, tablets and injection tablets are shown, and creams or face creams are also shown, applied 1-3 times a day to the skin in the spinal area.
- musorelaxant. The preparations for this group are ideal for increasing muscle tone, relaxing muscle fibers from transverse fractures and promoting the patient’s condition. On average, the treatment process is about 1 month. There are serious symptoms and treatment begins with the injection form of the medication. The dose must be increased gradually from the smallest, until the therapeutic effect is reached, and then gradually reduced to complete the cancellation.
Several other groups are used as other drugs:
- Vitamin. Accelerate the tissue recovery process, normalize the neural conductivity, accelerate metabolism, etc. These medications for osteocartilage are almost always prescribed in the form of injection, courses for 10 days. These are vitamins B1, B2, B6, E.
- Blood preparation. These drugs normalize blood flow in the blood and arteries, restore muscle tone of blood vessels, and restore metabolism. Most of the time, use the tablet release form. These drugs are treated for 1 to 3 months. Likewise, in extreme cases, the drug can be injected for the first 5-10 days, followed by a transition to the tablet.
- Glucocorticoid. They have anti-inflammatory, inflatable effects that enhance the work of NSAID and muscle relaxants. Depending on the severity of the patient's condition, their prescription is in the form of oral administration in the form of intramuscular or intramuscular or velocity or tablets. From days to weeks, choose the treatment process separately. The abolition of this drug should gradually decrease with the dose.
- Biostimulant. Accelerate metabolism, stimulate tissue recovery, reduce inflammation and swelling of tissues, etc. Most commonly used in injection form, while in tablets or other oral administration forms are not common. Depending on the severity of the disease, the treatment process may range from 1 week to 2-3 months.
Physical treatment of osteochondrosis
Physical therapy measures are used in combination with medications, allowing you to speed up the recovery process and extend the remission cycle when used outside of deterioration. There are many physical therapy methods, most of which are well practiced in treatments in osteocartilage:
- Electrophoresis. Based on the medications used during the process, analgesic effects were obtained. Metabolic improvement and normalization of blood flow in affected tissues.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture). With the help of special and best needles and their effects on the active points on the patient's skin, analgesic effects are achieved, and the recovery and metabolic processes are stimulated and inflammation is reduced.
- Magnetic therapy. Reduce tissue pain, swelling and inflammation, accelerate neural conductivity, and normalize metabolic processes
- Manual therapy. Recover mobility in the joints of the spine and reduces pain syndrome.
- massage. Normalize muscle tone, eliminate back pain, and restore nerve conductivity.
- Exercise therapy. Restores spine mobility, relieves pain, restores the usual lifestyle, strengthens the muscle frame of the back, relaxes the back muscles, and accelerates metabolism.
- The traction of the spine. Restore spinal mobility, prevent disease and complications, and anesthetize.
- Laser therapy. Improves blood supply, stimulates tissue regeneration, reduces pain and inflammation, and reduces swelling in the spine.
- Heat therapy. Anesthesia effects, normalization of blood flow and lymph nodes passing through blood vessels, reduction of inflammation in tissues, and acceleration of cartilage recovery.
- Mud (elastic therapy). Reduces spinal pain, reduces muscle cramps, slightly reduces the inflammatory process, and improves blood supply and metabolism.
One patient can be prescribed for 1 physical therapy event and its complex. This depends on the severity of osteochondrosis and the accompanying pathology. The duration of the treatment process is on average 10-15 days. It is recommended to repeat 3-4 times during the year. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the frequency of aggravation and the speed of progression of osteochondrosis multiple times.























